![[Home]](/chips.gif) G74 - Peck Drilling/Face Grooving
G74 - Peck Drilling/Face Grooving
... [RS274NGC] ... # REMAPPING REMAP=g74 modalgroup=1 argspec=xzk py=g740 ... [PYTHON] TOPLEVEL = python/toplevel.py PATH_PREPEND = python ...
#!/usr/bin/python import remap
#!/usr/bin/python from interpreter import INTERP_OK import math def g740(self, **words): # G74 is typically called like so: # G74 x ? z ? k ? (x = diameter, usually 0; z = hole endpoint; k = peck length) # get position if (self.params['_lathe_diameter_mode']): # if is_lathe_mode x_mode = 2 else: x_mode = 1 x_start = self.params[5420] * x_mode z_start = self.params[5422] if 'x' in words: x_end = words['x'] * x_mode else: x_end = x_start * x_mode if 'z' in words: z_end = words['z'] if z_end > z_start: return "G74 error - Z cannot be larger than the starting Z position" else: z_end = z_start if 'k' in words: peck_length = words['k'] if peck_length < 0: return "G74 error - K cannot be negative" else: peck_length = 0 if (self.params['_metric']): # if is_metric backoff_length = 0.50 # mm rounding_fudge = 0.0001 else: backoff_length = 0.020 # inch rounding_fudge = 0.00001 z_range = math.fabs(z_end - z_start) - rounding_fudge # rounding_fudge prevents extra peck if peck_length > 0: num_pecks = int(z_range / peck_length) else: num_pecks = 0 z_list = [] for i in range(num_pecks + 1): z_list.append(z_start - (i * peck_length)) z_list.append(z_end) #print "--kaw - z_list =", z_list if math.fabs(x_end - x_start) > rounding_fudge: # We're groove'n for i in range(num_pecks + 1): self.execute("G0 Z %s" % z_list[i]) self.execute("G1 Z %s" % z_list[i + 1]) self.execute("G1 X %s" % x_end) self.execute("G1 Z %s" % (z_list[i] + backoff_length)) self.execute("G0 X %s" % x_start) else: # We're drilling for i in range(num_pecks + 1): self.execute("G1 Z %s" % z_list[i + 1]) self.execute("G0 Z %s" % (z_list[i + 1] + backoff_length)) self.execute("G0 Z %s" % z_start) return INTERP_OK
The G74 routine above relies on an initial move to a starting position. This position is captured and used for x_start and z_start. The X and Z words in the G74 command are used for x_end and z_end. If x_start and x_end are equal, this invokes a plunge with chip break routine, otherwise a grooving routine is invoked. Since Python can round off floating point numbers, a "close enough" algorithm is use to test x_start and x_end equality. A check for peck_length > 0 is used to prevent a divide by zero error in the num_pecks calculation. Apparently, the x position parameter 5420 does not follow the lathe diameter mode, so we need to check for it and adjust x values. This needs testing, so beware. The z_range is adjusted a tiny bit so that an extra peck doesn't get added to the end. The peck algorithm counts the number of full pecks in z-range then adds a final z position of z_end. If the peck length fits evenly in z_range, the last full peck will happen to be at z_end, which we don't need because it's added later.
Peter Smid's book "CNC Programming Handbook, 3rd Edition" Page 222, covering G74 was used as a reference: https://books.google.com/books?id=w7-jBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA222
Parameters are:
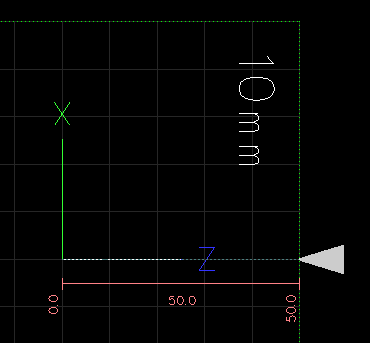 |
(G74 Peck Drilling Example) G7 (Dia. Mode) G18 (XZ Plane) G90 (Absolute Distance Mode) G40 (Turn Cutter Compensation Off) G21 (units in inches) G54 (Work Offset) G30 Z #5422 (Park Tool) T 0707 S 500 (RPM) M8 (Coolant ON) M3 (Spindle ON, Forward) G0 X 0.000 G0 Z 25.000 G74 Z 0.000 K 8 F 200 M9 (Coolant OFF) M5 (Spindle OFF) G30 Z #5422 (Park Tool) M30 (End of Program) |
|
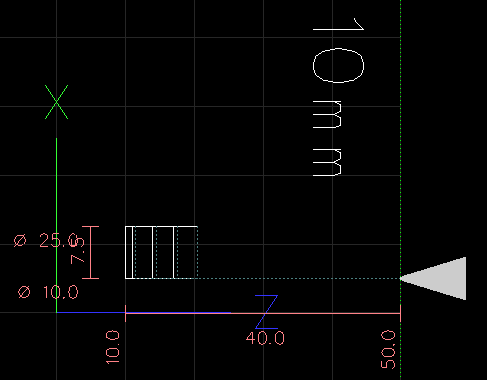 |
(G74 Grooving Example) G7 (Dia. Mode) G18 (XZ Plane) G90 (Absolute Distance Mode) G40 (Turn Cutter Compensation Off) G21 (units in inches) G54 (Work Offset) G30 Z #5422 (Park Tool) T 0707 S 500 (RPM) M8 (Coolant ON) M3 (Spindle ON, Forward) G0 X 10.000 G0 Z 20.000 G74 X 25.000 Z 10.000 K 3 F 200 M9 (Coolant OFF) M5 (Spindle OFF) G30 Z #5422 (Park Tool) M30 (End of Program) |
| Peck Drill Example | Grooving Example | |||
... [RS274NGC] ... # REMAPPING REMAP=g74 modalgroup=1 argspec=xzk ngc=g740 ...
o<g740>sub (Peck Drill) (capture start position) #<x_start> = #5420 (Current X Location) #<z_start> = #5422 (Current Z Location) #<z_end> = #<z> #<peck> = #<k> #<z_range> = [ABS[#<z_end> - #<z_start>]] #<num_pecks> = [#<z_range> / #<peck>] o10 if [#<peck> GT 0] #<num_pecks> = [#<z_range> / #<peck>] o10 else #<num_pecks> = 0 o10 endif o20 if [#<_metric>] #<back_off> = 0.500 (mm) o20 else #<back_off> = 0.0200 (inch) o20 endif #<pass> = 1 o30 repeat [#<num_pecks>] #<z_target> = [#<z_start> - [#<pass> * #<peck>]] G1 Z #<z_target> G0 Z [#<z_target> + #<back_off>] #<pass> = [#<pass> + 1] o30 endrepeat G1 Z #<z_end> G0 Z #<z_start> o<g740> endsub M2
#!/usr/bin/python import sys import linuxcnc from interpreter import INTERP_OK import math import emccanon def g740(self, **words): # G74 is typically called like so: # G74 x ? z ? k ? (x = diameter, usually 0; z = hole endpoint; k = peck length) # get machine G30 position in current G20/21 units x_start = self.params[5420] z_start = self.params[5422] if 'z' in words: z_end = words['z'] else: z_end = z_start if 'k' in words: peck_length = words['k'] else: peck_length = 0 z_range = z_end - z_start if peck_length > 0: num_pecks = int(math.fabs(z_range / peck_length)) else: num_pecks = 0 if (self.params['_metric']): # if is_metric backoff_length = 0.50 # mm else: backoff_length = 0.020 # inch for i in range(num_pecks): z_target = z_start - ((i + 1) * peck_length) line = i * 2 emccanon.STRAIGHT_FEED(line,x_start,0,z_target,0,0,0,0,0,0) emccanon.STRAIGHT_TRAVERSE(line + 1,x_start,0,(z_target + backoff_length),0,0,0,0,0,0) emccanon.STRAIGHT_FEED(line + 1,x_start,0,z_end,0,0,0,0,0,0) emccanon.STRAIGHT_TRAVERSE(line + 2,x_start,0,(z_start),0,0,0,0,0,0) return INTERP_OK